accuracy of acetabular labrum tear tests trial|acetabular labral treatment : importer Labral tears have been well documented in people with hip dysplasia [7, 39, 50, 73, 76]. In a study of patients with mild-to-moderate hip dysplasia and hip pain, McCarthy and Lee found that 72% of the 170 hips studied had labral tears, and 93% of these tears were in the anterior region of the labrum [76]. This page titled 2.3.1.2: Adding Antibiotics is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Nathan Reyna, Ruth Plymale, & Kristen Johnson.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Shopee Health & Beauty Medical Supplies Others 1500mL Autoclavable Green Bowls - 10QWORK Stainless Steel Instrument Tray Organizer with Lid, 2 Pack, 8" Container, Instruments Solid Box, Square Sterilization Box Container for Lab Instrument Supplies
A more recent study in those with acetabular labral tear has shown that conservative management over the course of 1 year with corticosteroid injection, activity modification, and physical therapy led to improved functional outcomes, and 71% of patients . A more recent study in those with acetabular labral tear has shown that conservative management over the course of 1 year with corticosteroid injection, activity modification, and physical therapy led to improved functional outcomes, and 71% of patients were satisfied with nonsurgical treatment.
The purpose of this study was to determine (1) the diagnostic accuracy of MRI and MRA for the detection of ALT, (2) whether 1.5 T or 3.0 T is all acceptable, by conducting a meta-analysis of the literature regarding the diagnostic performance of MRI/MRA.Labral tears have been well documented in people with hip dysplasia [7, 39, 50, 73, 76]. In a study of patients with mild-to-moderate hip dysplasia and hip pain, McCarthy and Lee found that 72% of the 170 hips studied had labral tears, and 93% of these tears were in the anterior region of the labrum [76].
For MRI (eight studies), the pooled sensitivity for detecting acetabular labral tears was 66% (95% CI 59 to 73) and pooled specificity was 79% (95% CI 67 to 91). For MRA (15 studies), the pooled sensitivity was 87% (95% CI 84 to 90) and pooled specificity was 64% (95% CI 54 to 74).The objective of the study was to determine diagnostic accuracy and validity of the patient history, physical examination and imaging for the diagnosis of acetabular labral tears in patients presenting with hip pain.
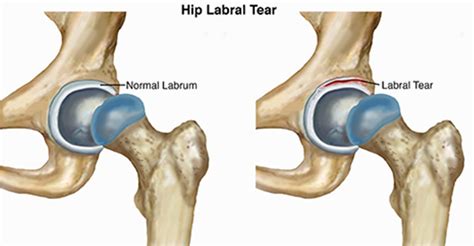
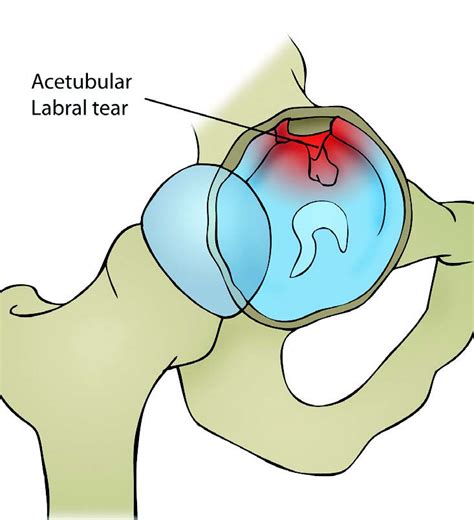
Acetabular labral tears may occur because of abnormal bony morphology (femoroacetabular impingement or secondary proximal femoral deformity), dysplasia, capsular laxity, trauma, or degeneration. We included all diagnostic accuracy studies that directly compared within-study, the accuracy of MRI or MRA (the index tests), to either arthroscopic or open surgical findings (the reference test) relating to acetabular labral tears.
The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only .
With physiotherapy, the mean iHOT12 score of the 35 patients with acetabular labral tears showed significant improvement from 44.0 to 73.6 ( P <0.001) in 4.7 months. Of these 35 patients, eight patients (22.9%) underwent surgical .Park SY et al. compared the diagnostic accuracy of three-dimensional intermediate-weighted fast spin-echo sequence and two-dimensional fast spin-echo sequences for the diagnosis of acetabular labral tears, and they found that Se and Sp were 0.74 and 0.89 for two-dimensional fast spin-echo sequences, and 0.78 and 0.92 for three-dimensional . A more recent study in those with acetabular labral tear has shown that conservative management over the course of 1 year with corticosteroid injection, activity modification, and physical therapy led to improved functional outcomes, and 71% of patients were satisfied with nonsurgical treatment. The purpose of this study was to determine (1) the diagnostic accuracy of MRI and MRA for the detection of ALT, (2) whether 1.5 T or 3.0 T is all acceptable, by conducting a meta-analysis of the literature regarding the diagnostic performance of MRI/MRA.
Labral tears have been well documented in people with hip dysplasia [7, 39, 50, 73, 76]. In a study of patients with mild-to-moderate hip dysplasia and hip pain, McCarthy and Lee found that 72% of the 170 hips studied had labral tears, and 93% of these tears were in the anterior region of the labrum [76].
would serological pipettes be equipment or materials
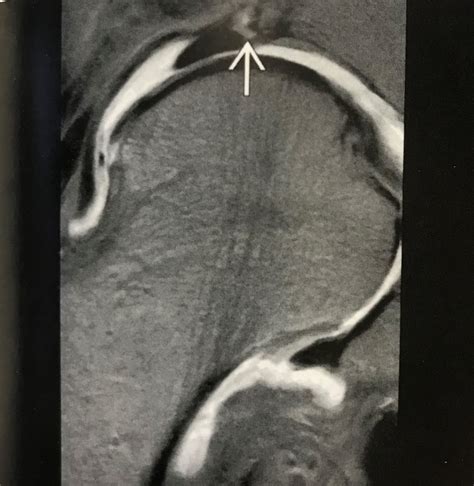
mri for acetabular labral tears
For MRI (eight studies), the pooled sensitivity for detecting acetabular labral tears was 66% (95% CI 59 to 73) and pooled specificity was 79% (95% CI 67 to 91). For MRA (15 studies), the pooled sensitivity was 87% (95% CI 84 to 90) and pooled specificity was 64% (95% CI 54 to 74).The objective of the study was to determine diagnostic accuracy and validity of the patient history, physical examination and imaging for the diagnosis of acetabular labral tears in patients presenting with hip pain.
Acetabular labral tears may occur because of abnormal bony morphology (femoroacetabular impingement or secondary proximal femoral deformity), dysplasia, capsular laxity, trauma, or degeneration. We included all diagnostic accuracy studies that directly compared within-study, the accuracy of MRI or MRA (the index tests), to either arthroscopic or open surgical findings (the reference test) relating to acetabular labral tears.The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only .
With physiotherapy, the mean iHOT12 score of the 35 patients with acetabular labral tears showed significant improvement from 44.0 to 73.6 ( P <0.001) in 4.7 months. Of these 35 patients, eight patients (22.9%) underwent surgical .
acetabular labrum hip surgery
would you use density to calibrate a volumetric pipette
Autoclavable up to 250 degreesF, 15 pounds of pressure for 15 to 20 minutes; The blue color makes it easy to identify; Extra large bedpan features a .Nothing that happens in the labor other workplace is as important as your health and safety. .
accuracy of acetabular labrum tear tests trial|acetabular labral treatment